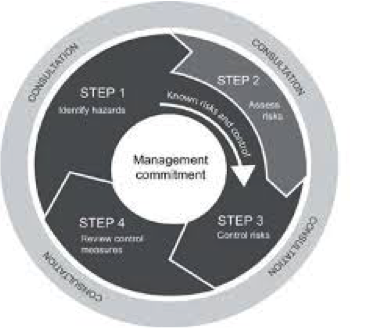
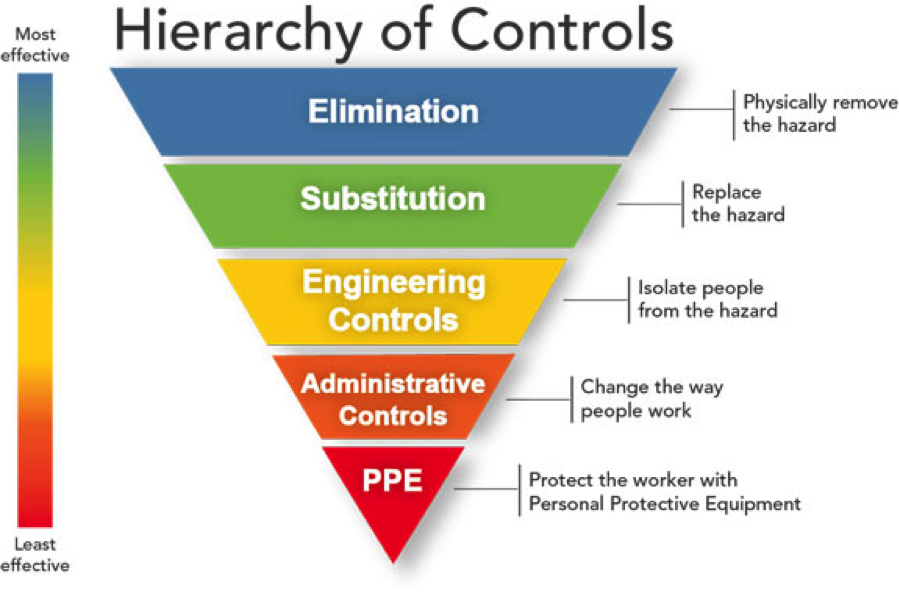
Under the Work Health and Safety Act 2011, Employ Me has a “Duty of Care” to ensure, so far as is reasonably practical, the health and safety of all employees and contractors. To ensure your health and safety, Employ Me will: – Provide a person as the nominated Responsible Officer for every project – Provide all contractors with a site specific (local) induction by the responsible officer prior to commencing work, which will address local hazards – Monitor the activities of contractors – Require contractors to provide suitable risk assessments / safe work procedures for performing all works SAFETY IS OUR PRIORITY Employ Me believes in and recognises the importance of safeguarding the health, safety and welfare of all employees and contractors. As far as is reasonably practical, Employ Me will take a proactive and preventative approach in safeguarding the community in respect of health and safety and take all reasonable actions to protect against unsafe conditions and work hazards. There are many safety issues to consider when undertaking any work on various Employ Me job sites. It is important to be aware of and understand the possible safety issues that need to be considered, as this will assist in ensuring everybody’s safety. General Induction Training consists of the knowledge and skills described in the unit of competency “Work safely in the construction industry” The training will include at least the following health and safety topics: -Duty of care under common law -Rights, responsibilities and enforcement provisions under OHS legislation -Mechanisms for raising issues and reporting unsafe conditions -Role and function of OHS representatives, committees or other OHS consultation arrangements -Identify hazards -Assess risks -Control risks (including the hierarchy of control) -Monitor and review General Induction training continued… -Manual handling -Hazardous substances (including asbestos) and dangerous goods -Noise national code of practice for induction for construction work 14 – Plant and equipment (including inspection, maintenance, licensing requirements) -UV radiation -Electrical safety -Traffic and mobile plant -Working at heights (including falling objects) -Excavations (including trenches) -Confined spaces -Unplanned collapse – Hot and cold working environments -Infectious diseases General Induction training continued… -OHS management plans -Work method statements, material safety data sheets, safety signs -Drugs and alcohol -Amenities – Smoking -Bullying/harassment -Housekeeping -Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) -First-aid -Accident & incident reporting -Emergency procedures – Workers’ compensation and injury management -Duty of care under common law -Rights, responsibilities and enforcement provisions under OHS legislation Your responsibilities include: -Providing reasonable care that what you do, or fail to do, does not adversely affect the health and safety of others -Complying with any reasonable instructions given to you by the Responsible Officer or their representative, and all security and safety instructions of the work site -Ensuring that you have licences, qualifications and training for the work that you will be undertaking -Ensuring that all plant and equipment is well maintained and in good working order -Wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) -Mechanisms for raising issues and reporting unsafe conditions HOW TO RAISE OHS ISSUES IN THE WORKPLACE SAFETY REPRESENTATIVES AND COMMITTEES Employees have the right to have a workplace occupational safety committee with elected employee representatives and appointed employer representatives. Employees also have the right to elect a safety and health representative. Consultation about safety and health matters is an important part of the Safety Representatives role. Safety Representatives are elected by the workforce and must complete an accredited course with in the first 12 months of assuming the position. Safety and Health Representative Roles include: -Identify hazards -Assess risks -Control risks (including the hierarchy of control) -Monitor and review HAZARD MANAGEMENT PROCESS A hazard is defined as something that has the potential to harm the health, safety and welfare of people at a workplace. A risk is defined as the likelihood that a hazard will cause injury, illness or disease, and the severity of the injury, illness or disease that may result. In order to minimise the risk of hazards in the workplace, contractors must undertake a risk management process. There are 4 steps to the risk management process: 4. Review of the control: Ask yourself is the chosen control effective and are there any new hazards that have been discovered as a result. CONTROLLING RISKS Once the risk arising from each hazard has been assessed, it must be eliminated, or if this is not possible, controlled. This is achieved using control measures that are set out in the hierarchy of controls. The hierarchy of controls provides the preferred method for eliminating or reducing the risk associated with a hazard. These controls must be implemented in the order specified, or if no single control is sufficient, then in combination should be used to minimise the risk: -Manual handling -Asbestos Awareness -Hazardous substances (including asbestos) and dangerous goods -Noise national code of practice for induction for construction work 14 – Plant and equipment (including inspection, maintenance, licensing requirements) -UV radiation -Electrical safety -Traffic and mobile plant -Working at heights (including falling objects) -Excavations (including trenches) -Confined spaces -Unplanned collapse – Hot and cold working environments -Infectious diseases MANUAL HANDLING Manual handling refers to any activity where a person exerts a force to lift, lower, push, pull, carry, or otherwise move, hold or restrain an object. Most tasks on a job site involves some form of manual handling. Using incorrect techniques can lead to injury. Actions you can take to reduce risks associated with manual handling include: -Minimise the lifting and lowering forces you exert -Avoid the need for bending, twisting and reaching movements -Reduce pushing, pulling, carrying and holding -Reduce repetitive and sustained movements -Wherever possible mechanical aids should be used to minimise any manual handling -Divide the load -Seek assistance where the item is to heavy and no mechanical aids suitable ASBESTOS Asbestos is dangerous, and work involving asbestos must be performed with care. Any traces of asbestos needs to be reported to your Responsible Officer and appropriate steps should be taken to assure your safety and those working on the site. In areas where you suspect you may encounter asbestos, Facilities and Services have a register of asbestos locations which must be referred to. Under the Work Health and Safety Act 2011, Worksafe ACT require all construction workers (as well as workers in some other occupations) to complete the Asbestos Awareness 10314 NAT course within Australian Capital Territory. Asbestos – some job sites contain asbestos. This is recorded on the Asbestos Register. No work to be performed without authorisation. If suspected asbestos discovered, contact your Responsible Officer. TYPES OF HAZARDS Remember, a hazard is anything with the potential to cause damage to people, the environment, property, plant or equipment. ALL WORKERS ARE OBLIGED TO REPORT HAZARDS TO THEIR SUPERVISOR or PERSON IN CHARGE OF THE WORKPLACE Types of hazards that may be encountered on job sites include: Occupational Noise – Some job sites require Hearing Protection .Do not enter unless wearing appropriate hearing protection. Hazardous Chemicals – many job site activities involve use of chemicals which can be harmful to health. Do not enter any work area without authorisation of person in control. It is important that the requirements set out in an MSDS are strictly followed by all personnel at all times. For every hazardous substance in the workplace there must be an accompanying MSDS which must be accessible to everybody and should be located near where the substance is being used or stored. A MSDS register must be developed and constantly be updated. Traffic Hazards – Roads utilised by range of vehicles from cars to heavy vehicles. Maintain situational awareness at all times. Pedestrians use footpaths and crossings where possible. Drivers observe speed limits and parking restrictions. Beware of areas where forklifts are operating and observe pedestrian markings. TYPES OF HAZARDS continued Confined spaces – A confined space could be a manhole, excavation, inside a storage tank, or a sewer pit. Employees should have received adequate training and certification before entering into a confined space. Excavations and trenches – All trenches must be barricaded of fenced off to warn people of their location, and to prevent accidental or unauthorised entry. People should not enter areas immediately next to trenches or excavations unless the area is well signed and are authorised to be there. When excavation work is to be carried out and buried power cables or gas pipelines could be in the vicinity, their location must be identified and approval must be obtained prior to work commencing and a risk assessment conducted. Plant and Machinery – Avoid entering any areas where plant and machinery are located or operating. Not to be used without proper authorisation. Slips, Trips and Falls – maintain situational awareness when walking around job sites. Use handrails where provided. Consider appropriate footwear for the environment. TYPES OF HAZARDS continued Working at heights – This includes any work on; working on the roofs of buildings, working from elevated work platforms or scaffolding, working near the edge of excavations, and working from ladders. All employees need to be properly trained and certified to work at heights. Fall arrest/ restraint equipment must be provided to all persons who work where there is a danger of falling from heights. All height safety equipment must be inspected prior to its use and regularly re-checked as required by the relevant Standard and manufacturer’s instructions. Unplanned collapse- An unplanned collapse can pose a significant danger to construction workers. An unplanned collapse can include: The collapse of a building or structure (or part of) which is unstable before completion or demolition, Failure of a load bearing part of a crane, hoist, lifting gear or lift, the collapse of an excavation. To reduce the likelihood of injury you should be aware of any potential hazards and comply with all workplace procedures, including complying with maximum load limits and not entering exclusion zones. Hot and cold working conditions- Weather conditions can have a big impact upon the safety and health of workers, especially in outdoor work environments. Some weather conditions will be immediately obvious such as rain or gusts of wind, others such as exposure to prolonged heat or cold are dangerous and the impact may not be realised until the damage is done. Workplaces must have safe work practices for whatever situation workers are in and have contingency plans that accommodate changing weather conditions. TYPES OF HAZARDS continued Electrical safety– Contact with energised objects at mains voltages is potentially fatal. It can also cause serious burns from the discharge of electrical energy. Health effects include muscle spasms, shock, burns, nausea and vomiting, palpitations, heart fibrillation, unconsciousness. Always assume all electrical appliances are “live” until they are effectively isolated. Isolate, tag and test equipment before commencing work. Do not use defective equipment. Remove it from use, tag it out and report it. Make sure the power is off before removing a plug from a power point. Remove the plug by firmly grasping the plug & not the cable. Switch the power off before changing light bulbs. Do not operate portable electrical equipment while out in the rain or other wet areas. Infectious diseases – Most workplaces have minimal risk of the transmission of infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis or other viruses. Where there is a possibility that workers will be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids, there is a potential for the transmission of viruses. You should ensure that; You don’t do anything which may expose you or another person to an infectious disease. Dispose of infectious material safely ( a syringe collection devise ,sanitary waste). Use good housekeeping and personal hygiene. Use the right cleaning materials. Use appropriate PPE. Cover wounds, cuts and abrasions with dressings. TYPES OF HAZARDS continued UV Radiation – Using this cream helps prevent the suns rays penetrating the skin.Sunlight contains ultraviolet (UV) radiation which causes premature aging of the skin, wrinkles, eye damage (including cataracts), and skin cancer. The amount of damage from UV exposure depends on the UV radiation levels (which can range from low to extreme), the length of the exposure and whether your skin is protected. There can be high levels even on cool days and you can receive sunburn on a cloudy day. Sun exposure at any age can cause skin cancer. The most dangerous form of skin cancer is melanoma. Australia has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world. -OHS management plans -Work method statements, material safety data sheets, safety signs WORKPLACE DOCUMENTATION There are several types of OHS documents that should be at the workplace. These documents provide information about health and safety information in the workplace and provide a way hazards, incidents and injuries can be reported. You as an employee or subcontractor have a right to inspect these documents in the workplace Examples of these documents include: This document gives an overall view of the hazards that could be encountered at the site and the planned method to control these hazards. It will also include the points of contact after hours and in case of emergency. This is used in conjunction with the JSA. MSDS exists for materials that are hazardous. The sheets are supplied by the manufacturer or supplier and act as a register of all hazardous materials at the workplace. A register of all JSAs on the site should be maintained and available upon request by all employees. These forms should be readily available at the site and must be completed in the event of an accident, incident or injury at site. Hazard report forms should be readily available to all persons on site. Employees should be encouraged to complete a hazard report form and pass to their supervisors as soon as practicable. -Alcohol and Drugs -Smoking -Mobile Phones -Confidentiality -Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) -Bullying/harassment -Housekeeping Alcohol and Drugs It is strictly prohibited to consume alcohol or use illegal drugs whilst working. If you are observed being under the influence of alcohol or illegal drugs at a worksite, you will be terminated at once and will be directly responsible for any injuries or accidents caused while under the condition. Smoking The majority of companies prohibit smoking at job sites. Though some of them may provide a smoking area. Make sure that you comply with workplace policy. Mobile Phones The majority of companies prohibit the use of mobile phones while working at a job site. Mobile phones may be used during breaks including smokos and lunchtimes. You will be directly responsible for any injuries or accidents caused while using mobile phones during physical working hours on the job site. Make sure that you comply with workplace policy. Confidentiality All the personal information requested serves only for the purpose of registering the employee to the database for quick evaluation of suitability for the position. All information is securely held within the office and is accessible only to authorised personnel. We will not disclose your personal information to any third parties unless disclosure is required by law. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Where hazards cannot be eliminated by other means it is a requirement of occupational and safety legislation that all employees wear personal protective equipment in working environments. * Employees are to use the PPE and equipment in the manner in which they have been instructed to. * Employees are not to misuse or damage the clothing and equipment. * Employees must maintain the PPE if appropriate. * Employees must, as soon as possible after becoming aware of any damage or malfunction to the PPE, notify the employer of such damage etc. Bullying/harassment Harassment, discrimination and bullying are significant workplace issues that impact on workplace efficiency and employees’ physical and mental health. The Organisation supports a workplace that is free from harassment, discrimination and bullying and supports equality of opportunity and values diversity in employment. The Organisation recognises the right of all employees to work in an environment free from harassment, bullying and unlawful discrimination and these behaviours will not be tolerated. HOUSEKEEPING The worksite and surrounding areas must be kept clean and tidy at all times, and any safety or fire hazards must be removed promptly (e.g. oily rags, flammable materials and garbage). Rubbish must be removed progressively to an appropriate skip bin on site, or to an appropriately licensed Waste Management Facility. Employees should also remember safety actions such as: – Replacing lids and caps on containers – Wiping up spills – Removing or bending-over nails or bolts – Removing other dangerous or protruding objects -First-aid -Fire Safety -Accident & incident reporting -Emergency procedures -Workers compensation and injury management FIRST AID Your employer has a legal responsibility to provide adequate First Aid equipment and facilities in the workplace. This includes access to trained first aiders. A designated person should be appointed to be in charge of the First Aid kit, they must be ready to provide first aid when necessary. You should know the name, contact number and workplace location of the first aid officer or person to contact, if you don’t know ASK. Your worksite should also have a first aid plan that details workplace first aid procedures, and the location of first aid equipment as part of the site specific safety management plan FIRE SAFETY EQUIPMENT When working on job sites, it is important you familiarise yourself with the location of break-glass alarms, fire extinguishers and emergency exits. The locations of fire safety equipment can be found on the Emergency Maps located at site offices. ACCIDENT AND INJURY REPORTING If someone is injured at work, providing them with immediate assistance is of the utmost importance. However you should only administer assistance to the level you have been trained, (e.g. If you have received first aid training), and ONLY if you feel competent and it is safe to do so. All employees must report to their supervisor as soon as practically possible any injury or harm to themselves or any other person in the workplace and any potential serious occurrence that in the course of or in connection with their work any situation they believe is a hazard in the workplace. Accurate and prompt reporting of injuries, serious occurrences and hazards is fundamental to maintaining a safe and healthy workplace. However, it is essential that all accidents, incidents and identified hazards are reported to Employ Me Representatives as soon as possible. Some serious incidents are required to be notified to WorkSafe ACT. It is very important that the incident site not be disturbed in these circumstances because WorkSafe may need to conduct an investigation. Follow the link for more information about incident reporting. (please link to https://lcms.elmolms.com/live_modules/course_835_ZWRzZ2RwNEkzZzNrmJk=/pages/images/AWS_37568_Accident_Reporting_Poster-WS-Update.pdf EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Assembly points / muster areas and evacuation routes will be pointed out during local site induction. It is important to remember where these areas are, in the event of a fire or other emergency. – Evacuation alarms on job sites may be a sound or bells. – If the evacuation alarm is activated, immediately cease work, exit the job site and walk to the nearest Evacuation Assembly Area. – In the event of a job site evacuation, follow directions given by Wardens and report to the Warden at the Assembly area for Roll Call. – Do not re-enter the job site or leave the assembly area until instructed to do so by your Responsible Officer or Incident Controller. – Ensure that your vehicle/s and/or equipment do not block access for emergency vehicles. -All personnel are to follow directions given by their Responsible Officer in a job site emergency. If required to evacuate, it is important that all employees follow the evacuation procedures and instructions from Emergency Wardens and/or Security Services. It is also important that you report to your supervisor for a head-count, to ensure all people are accounted for. Workers Compensation If you are injured at work Workers Compensation (Compo) means that you can receive medical treatment and assistance . All employees have a right to workers compensation. Workers Compensation will cover you for medical expenses and wages to varying degrees and dependant on your circumstances. There are defined procedures that you must follow to ensure that you do not jeopardise your entitlement to workers compensation, these include: Keep a copy of all relevant documents REVIEW OF INDUCTION This Induction has provided an overview of what you can expect when working on job sites. Throughout the Induction, we have looked at risk management principles, possible hazards that may be encountered and emergency procedures. Remember: In addition to this online Induction, you will also receive a local site induction when you arrive at any job site. You will be issued with an electronic Employ Me Induction certificate, which will be accessible from your online account. You must carry with you at all times your White Card, and any other relevant licences. For further information on Employ Me policies please contact our Employ Me Representative. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I acknowledge that I currently hold a White Card & Asbestos Awareness Certificate (if applicable) – I have undertaken General Induction Training in accordance with the National Code of Practice For Induction For Construction Work (if applicable). By entering my details to record my completion of the following knowledge test, I declare that I am the actual person who has undertaken the Employ Me Induction training module, and that I have understood its contents, and will abide by all of the requirements relevant to the tasks that I will perform for Employ Me. If, at any time, I act or behave in a manner which is in conflict to the requirements of Employ Me, I understand that I will be removed from the premises and prohibited entry until further notice or action has taken place. Assessment Instructions The assessment question format is multiple choice. There is only one correct answer. Select the correct answer by clicking on the corresponding button. Once you start the assessment you will not be able to navigate away from the questions without having to restart from the beginning.
It is your responsibility to keep your work area in a safe and working order.

